Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Electrolysis Modeling#
Objective#
This example demonstrates the modeling of a PEM electrolyzer using PyFluent. The simulation captures three-dimensional multiphase flow involving liquid water and a gas mixture, coupled with electrochemical reactions governed by Butler–Volmer kinetics. It includes dual potential fields representing electronic and ionic conduction, along with porous media transport through the catalyst and diffusion layers. The workflow employs the electrolysis model to simulate hydrogen and oxygen generation at the anode and cathode catalyst layers under a total cell voltage of 1.73 V. Liquid water enters the anode at 333.15 K with a mass flow rate of 0.000404 kg/s. The simulation is performed under steady-state conditions, initialized with full liquid saturation and a uniform temperature field.
Problem Description#
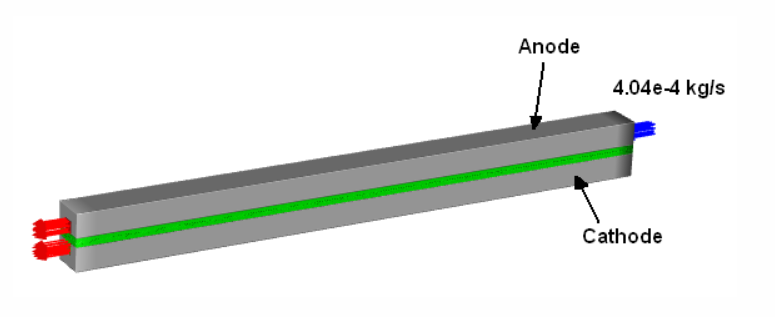
The 3D domain represents a PEM electrolyzer with an anode, membrane, and cathode assembly, including porous and catalyst layers, flow channels, and current collectors. Electrochemical reactions follow Butler-Volmer kinetics with OER at the anode and HER at the cathode. A VOF model captures gas-liquid flow, while porous media account for Darcy flow, capillary pressure, and contact angle effects. Dual conductivity represents both electronic and ionic transport, with osmotic drag modeling water transport through the membrane. The cell operates at 1.730202 V, with liquid water entering the anode at 333.15 K and 0.000404 kg/s.
Import modules#
Note
Importing the following classes offer streamlined access to key solver settings, eliminating the need to manually browse through the full settings structure.
import os
import ansys.fluent.core as pyfluent
from ansys.fluent.core import examples
from ansys.fluent.core.solver import (
BoundaryConditions,
Contour,
Controls,
Graphics,
Initialization,
Materials,
Mesh,
RunCalculation,
Setup,
)
Launch Fluent session in solver mode#
solver = pyfluent.launch_fluent(
precision=pyfluent.Precision.DOUBLE,
mode=pyfluent.FluentMode.SOLVER,
)
Download mesh file#
mesh_file = examples.download_file(
"electrolysis.msh.h5",
"pyfluent/electrolysis",
save_path=os.getcwd(),
)
solver.settings.file.read_mesh(file_name=mesh_file)
Display mesh#
graphics = Graphics(solver)
mesh = Mesh(solver, new_instance_name="mesh-1")
graphics.picture.x_resolution = 650 # Horizontal resolution for clear visualization
graphics.picture.y_resolution = 450 # Vertical resolution matching typical aspect ratio
all_walls = mesh.surfaces_list.allowed_values()
mesh.surfaces_list = all_walls
mesh.options.edges = True
mesh.display()
graphics.picture.save_picture(file_name="Electrolysis_Modeling_1.png")
Enable Electrolysis Model#
setup = Setup(solver)
setup.models.echemistry = {
"potential": True,
"echemistry_enabled": True,
"electrolysis": {
"options": {
"bc_type": "Total voltage",
"tot_voltage": 1.730202, # V
},
"parameters": {
"anode_jref": 1.36e-09, # A/m²
"anode_jea": 181411, # A/m²
"anode_exp": 0, # Concentration exponent
"cathode_jref": 200, # A/m²
"cathode_jea": 24359, # A/m²
"cathode_ex_a": 1, # Anodic transfer coefficient
"cathode_ex_c": 1, # Cathodic transfer coefficient
"open_voltage": 1.1999, # V
},
"anode": {
"anode_cc_zone": {
"anode_cc_zone_list": ["anode_cc"],
"anode_cc_material": "collector-default",
},
"anode_fc_zone": {"anode_fc_zone_list": ["anode_fc"]},
"anode_pl_zone": {
"anode_pl_zone_list": ["anode_pl"],
"anode_pl_material": "porous-default",
"anode_pl_porosity": 0.75, # Porosity of porous layer
"anode_pl_kr": 4.9e-11, # m² Absolute permeability
"anode_pl_angle": 70, # Degrees
},
"anode_cl_zone": {
"anode_cl_zone_list": ["anode_cl"],
"anode_cl_material": "catalyst-default",
"anode_cl_porosity": 0.2, # Catalyst layer porosity
"anode_cl_kr": 4.9e-12, # m² Catalyst layer permeability
"anode_cl_angle": 80, # Degrees
},
},
"electrolyte": {
"mem_zone": {
"mem_zone_list": ["mem"],
"mem_material": "electrolyte-default",
}
},
"cathode": {
"cathode_cc_zone": {
"cathode_cc_zone_list": ["cathode_cc"],
"cathode_cc_material": "collector-default",
},
"cathode_fc_zone": {"cathode_fc_zone_list": ["cathode_fc"]},
"cathode_pl_zone": {
"cathode_pl_zone_list": ["cathode_pl"],
"cathode_pl_material": "porous-default",
"cathode_pl_porosity": 0.75, # Porosity
"cathode_pl_kr": 1e-11, # m² Permeability
},
"cathode_cl_zone": {
"cathode_cl_zone_list": ["cathode_cl"],
"cathode_cl_material": "catalyst-default",
"cathode_cl_porosity": 0.2, # Catalyst layer porosity
"cathode_cl_kr": 2e-12, # m² Permeability
},
},
"electrical_tab": {
"anode_tab": ["anode_tab", "anode_tab.1", "anode_tab.1.1"],
"cathode_tab": ["cathode_tab", "cathode_tab.1", "cathode_tab.1.1"],
},
},
}
Define solid materials#
materials = Materials(solver)
# Current collector
materials.solid["collector-default"] = {
"electric_conductivity": {"value": 20000} # S/m
}
# Porous layer
materials.solid["porous-default"] = {"electric_conductivity": {"value": 20000}} # S/m
# Catalyst layer: dual conductivity
materials.solid["catalyst-default"] = {
"electric_conductivity": {"value": 5000}, # S/m Electronic
"dual_electric_conductivity": {"value": 4.5}, # S/m Ionic in catalyst
}
# Membrane: ionic conductivity
materials.solid["electrolyte-default"] = {
"dual_electric_conductivity": {"value": 11} # S/m Proton conductivity
}
Boundary conditions#
conditions = BoundaryConditions(solver)
# Mixture phase: thermal condition
conditions.mass_flow_inlet["anode_in"] = {
"phase": {"mixture": {"thermal": {"total_temperature": {"value": 333.15}}}} # K
}
# Phase-2 (liquid water): mass flow rate
conditions.mass_flow_inlet["anode_in"] = {
"phase": {"phase-2": {"momentum": {"mass_flow_rate": {"value": 0.000404}}}} # kg/s
}
Solution controls#
controls = Controls(solver)
controls.under_relaxation = {"mp": 1}
Initialize solution#
initialize = Initialization(solver)
initialize.initialization_type = "standard"
initialize.defaults = {
"temperature": 333.15, # K
"phase-2-mp": 1, # Initial volume fraction of liquid
}
Run calculation#
calculation = RunCalculation(solver)
calculation.iterate(iter_count=300)
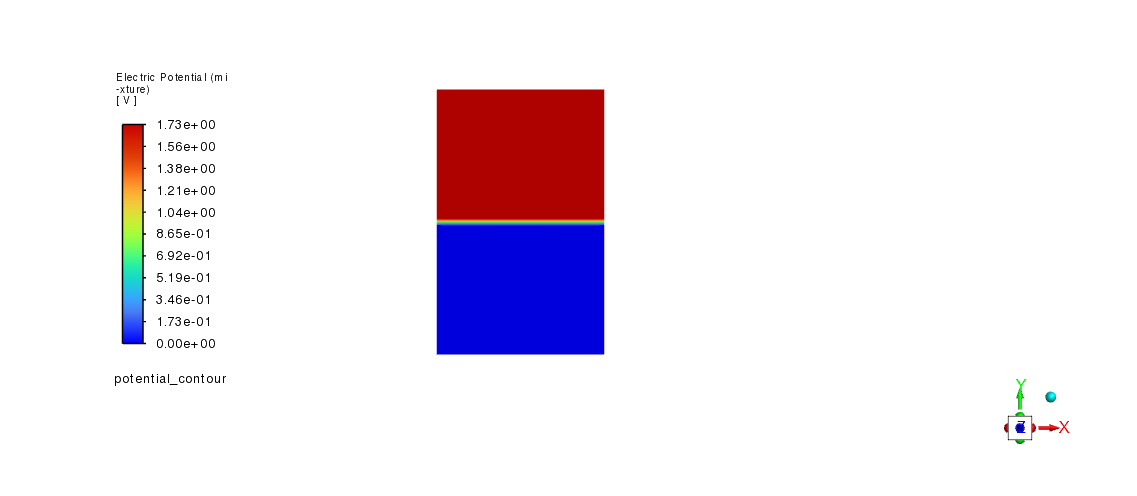
Post-processing#
potential_contour = Contour(solver, new_instance_name="potential_contour")
potential_contour.field = "potential"
potential_contour.surfaces_list = ["zmid"]
graphics.views.restore_view(view_name="front")
potential_contour.display()
graphics.views.restore_view(view_name="front")
graphics.picture.save_picture(file_name="Electrolysis_Modeling_2.png")
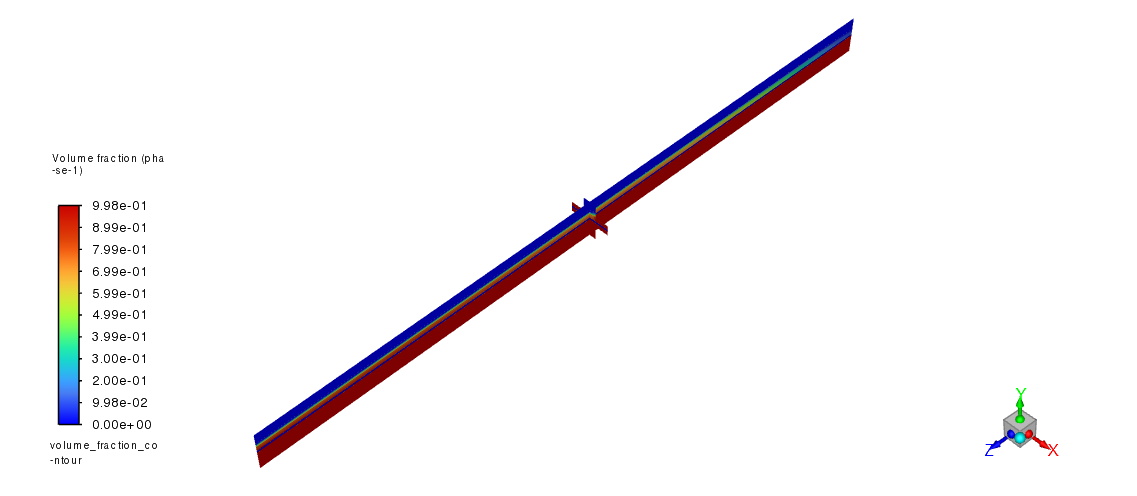
volume_fraction_contour = Contour(solver, new_instance_name="volume_fraction_contour")
volume_fraction_contour.field = "phase-1-vof"
volume_fraction_contour.surfaces_list = ["zmid", "xmid"]
graphics.views.restore_view(view_name="isometric")
volume_fraction_contour.display()
graphics.picture.save_picture(file_name="Electrolysis_Modeling_3.png")
# save case and data file
solver.settings.file.write(file_type="case-data", file_name="electrolysis")
Close session#
solver.exit()
Summary#
In this example, we used PyFluent to simulate a complete PEM electrolysis process under steady-state conditions. The model applies Butler-Volmer electrochemistry with a total cell voltage boundary condition and includes dual conductivity in catalyst layers, multiphase VOF flow, and porous media transport. Effects such as osmotic drag and capillary pressure capture water management within the cell. The workflow defines zones, assigns materials, sets inlet conditions, and solves for coupled electrochemical and flow fields.
References:#
[1] Electrolysis Modeling, Ansys Fluent documentation.

