Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Modeling Cavitation#
This example examines the pressure-driven cavitating flow of water through a sharp-edged orifice. This is a typical configuration in fuel injectors, and brings a challenge to the physics and numerics of cavitation models because of the high pressure differentials involved and the high ratio of liquid to vapor density.
This example uses the multiphase modeling capability of Ansys Fluent, and will be able to predict the strong cavitation near the orifice after flow separation at a sharp edge.
Workflow tasks
This example demonstrates how to do the following:
Set boundary conditions for internal flow
Use the mixture model with cavitation effects
Calculate a solution using the pressure-based coupled solver
Problem description
The problem considers the cavitation caused by the flow separation after a sharp-edged orifice. The flow is pressure driven, with an inlet pressure of 500 kPa and an outlet pressure of 95 kPa. The orifice diameter is 4 mm, and the geometrical parameters of the orifice are D/d = 2.88 and L/d = 4, where D, d, and L are the inlet diameter, orifice diameter, and orifice length respectively.
Example Setup#
Before you can begin, you must set up the example and initialize this workflow.
Launch Fluent#
Perform required imports, which includes downloading and importing the geometry file.
import os
import ansys.fluent.core as pyfluent
from ansys.fluent.core import examples
cav_file = examples.download_file(
"cav.msh.gz", "pyfluent/cavitation", save_path=os.getcwd()
)
Launch a Fluent session in the 2d solution mode with double precision running on four processors and print Fluent version.
solver_session = pyfluent.launch_fluent(
precision="double",
processor_count=4,
mode="solver",
dimension=2,
)
print(solver_session.get_fluent_version())
Read the mesh that was downloaded.
solver_session.settings.file.read_mesh(file_name=cav_file)
solver_session.settings.mesh.check()
Specify an axisymmetric model.
solver_session.settings.setup.general.solver.two_dim_space = "axisymmetric"
Enable the multiphase mixture model.
solver_session.settings.setup.models.multiphase.models = "mixture"
solver_session.tui.define.models.multiphase.mixture_parameters("no", "implicit")
Enable the k-ω SST turbulence model.
solver_session.settings.setup.models.viscous = {
"model": "k-omega",
"k_omega_model": "sst",
}
Define materials#
Create a material named water, using 1000 kg/m3 for density and 0.001 kg/m–s for viscosity. Then, copy water vapor properties from the database and modify the copy by changing the density to 0.02558 kg/m3 and the viscosity to 1.26e-06 kg/m–s.
solver_session.settings.setup.materials.fluid["water"] = {
"density": {
"option": "constant",
"value": 1000,
},
"viscosity": {
"option": "constant",
"value": 0.001,
},
}
solver_session.settings.setup.materials.database.copy_by_name(
type="fluid", name="water-vapor"
)
solver_session.settings.setup.materials.fluid["water-vapor"] = {
"density": {"value": 0.02558},
"viscosity": {"value": 1.26e-06},
}
Phases#
Change the name of the primary phase to “liquid” and the secondary phase to “water-vapor”. Then, enable the cavitation model and set the number of mass transfer mechanisms to 1. Finally, specify cavitation as a mass transfer mechanism occurring from the liquid to the vapor.
solver_session.tui.define.phases.set_domain_properties.change_phases_names(
"vapor", "liquid"
)
solver_session.tui.define.phases.set_domain_properties.phase_domains.liquid.material(
"yes", "water"
)
solver_session.tui.define.phases.set_domain_properties.phase_domains.vapor.material(
"yes", "water-vapor"
)
solver_session.tui.define.phases.set_domain_properties.interaction_domain.heat_mass_reactions.mass_transfer(
1, "liquid", "vapor", "cavitation", "1", "no", "no", "no"
)
Boundary Conditions#
For the first inlet momentum boundary conditions set the direction specification method to ‘normal to boundary’, gauge total pressure as 500 kPa and supersonic or initial gauge pressure as 449 kPa.
For the turbulence settings choose ‘Intensity and Viscosity Ratio’ for turbulent specification. Set turbulent intensity and turbulent viscosity ratio to 0.05 and 10 respectively.
inlet_1 = solver_session.settings.setup.boundary_conditions.pressure_inlet[
"inlet_1"
].phase
inlet_1["mixture"] = {
"momentum": {
"gauge_total_pressure": {"value": 500000},
"supersonic_or_initial_gauge_pressure": {"value": 449000},
"direction_specification_method": "Normal to Boundary",
},
"turbulence": {
"turbulent_specification": "Intensity and Viscosity Ratio",
"turbulent_intensity": 0.05,
"turbulent_viscosity_ratio": 10,
},
}
Before copying inlet_1’s boundary conditions to inlet_2, set the vapor fraction to 0.
inlet_1["vapor"] = {
"multiphase": {
"volume_fraction": {"value": 0},
},
}
solver_session.settings.setup.boundary_conditions.copy(from_="inlet_1", to="inlet_2")
For the outlet boundary conditions, set the gauge pressure as 95 kPa. Use the same turbulence and volume fraction settings as the inlets.
outlet = solver_session.settings.setup.boundary_conditions.pressure_outlet[
"outlet"
].phase
outlet["mixture"] = {
"momentum": {
"gauge_pressure": {"value": 95000},
},
"turbulence": {
"turbulent_specification": "Intensity and Viscosity Ratio",
"turbulent_intensity": 0.04,
"turbulent_viscosity_ratio": 10,
},
}
outlet["vapor"] = {
"multiphase": {
"volume_fraction": {"value": 0},
},
}
Operating Conditions#
Set the operating pressure to 0.
solver_session.settings.setup.general.operating_conditions.operating_pressure = 0
Solution#
To configure the discretization scheme, set ‘first order upwind’ method for turbulent kinetic energy and turbulent dissipation rate, ‘quick’ for the momentum and volume fraction, and ‘presto!’ for pressure.
methods = solver_session.settings.solution.methods
methods.discretization_scheme = {
"k": "first-order-upwind",
"mom": "quick",
"mp": "quick",
"omega": "first-order-upwind",
"pressure": "presto!",
}
For the pressure velocity coupling scheme choose ‘Coupled’. Set the pseudo time step method to ‘global time step’ and enable ‘High Order Term Relaxation’. Then, set the explicit relaxation factor for ‘Volume Fraction’ to 0.3.
methods.p_v_coupling.flow_scheme = "Coupled"
methods.pseudo_time_method.formulation.coupled_solver = "global-time-step"
methods.high_order_term_relaxation.enable = True
solver_session.settings.solution.controls.pseudo_time_explicit_relaxation_factor.global_dt_pseudo_relax[
"mp"
] = 0.3
To plot the residuals, enable plotting and set the convergence criteria to 1e-05 for x-velocity, y-velocity, k, omega, and vf-vapor. Enable the specified initial pressure then initialize the solution with hybrid initialization.
resid_eqns = solver_session.settings.solution.monitor.residual.equations
resid_eqns["continuity"].absolute_criteria = 1e-5
resid_eqns["x-velocity"].absolute_criteria = 1e-5
resid_eqns["y-velocity"].absolute_criteria = 1e-5
resid_eqns["k"].absolute_criteria = 1e-5
resid_eqns["omega"].absolute_criteria = 1e-5
resid_eqns["vf-vapor"].absolute_criteria = 1e-5
initialization = solver_session.settings.solution.initialization
initialization.initialization_type = "hybrid"
initialization.hybrid_init_options.general_settings.initial_pressure = True
initialization.hybrid_initialize()
Save and Run#
Save the case file ‘cav.cas.h5’. Then, start the calculation by requesting 500 iterations. Save the final case file and the data.
solver_session.settings.file.write_case(file_name="cav.cas.h5")
solver_session.settings.solution.run_calculation.iterate(iter_count=500)
solver_session.settings.file.write_case_data(file_name="cav.cas.h5")
Post Processing#
Since Fluent is being run without the GUI, we will need to export plots as picture files. Edit the picture settings to use a custom resolution so that the images are large enough.
graphics = solver_session.settings.results.graphics
# use_window_resolution option not active inside containers or Ansys Lab environment
if graphics.picture.use_window_resolution.is_active():
graphics.picture.use_window_resolution = False
graphics.picture.x_resolution = 1920
graphics.picture.y_resolution = 1440
Create contour plots#
Create a contour plot for static pressure, turbulent kinetic energy and the volume fraction of water vapor. For each plot enable banded coloring and filled option.
graphics = solver_session.settings.results.graphics
graphics.contour["contour_static_pressure"] = {
"coloring": {
"option": "banded",
"smooth": False,
},
"field": "pressure",
"filled": True,
}
Mirror the display around the symmetry plane to show the full model.
solver_session.settings.results.graphics.views.mirror_zones = ["symm_2", "symm_1"]
graphics.contour["contour_static_pressure"].display()
graphics.picture.save_picture(file_name="contour_static_pressure.png")
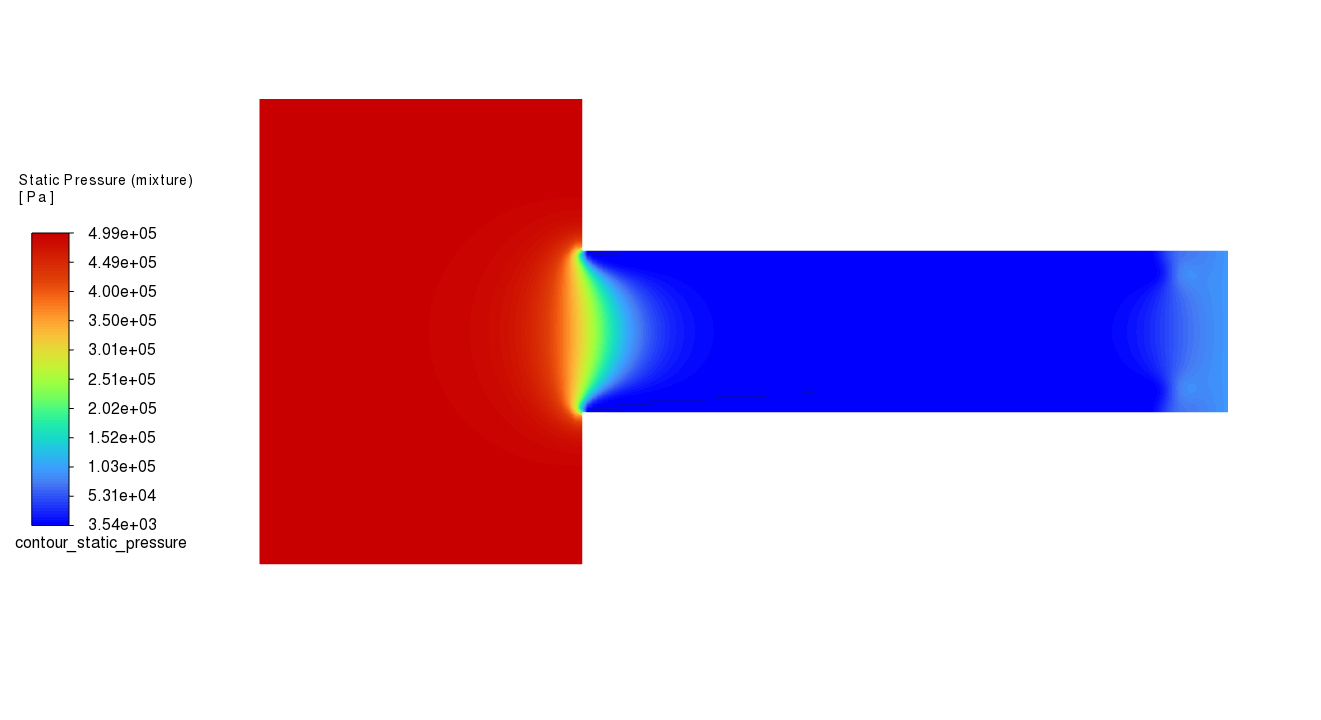
graphics.contour.create("contour_tke")
graphics.contour["contour_tke"] = {
"coloring": {
"option": "banded",
"smooth": False,
},
"field": "turb-kinetic-energy",
"filled": True,
}
graphics.contour["contour_tke"].display()
graphics.picture.save_picture(file_name="contour_tke.png")
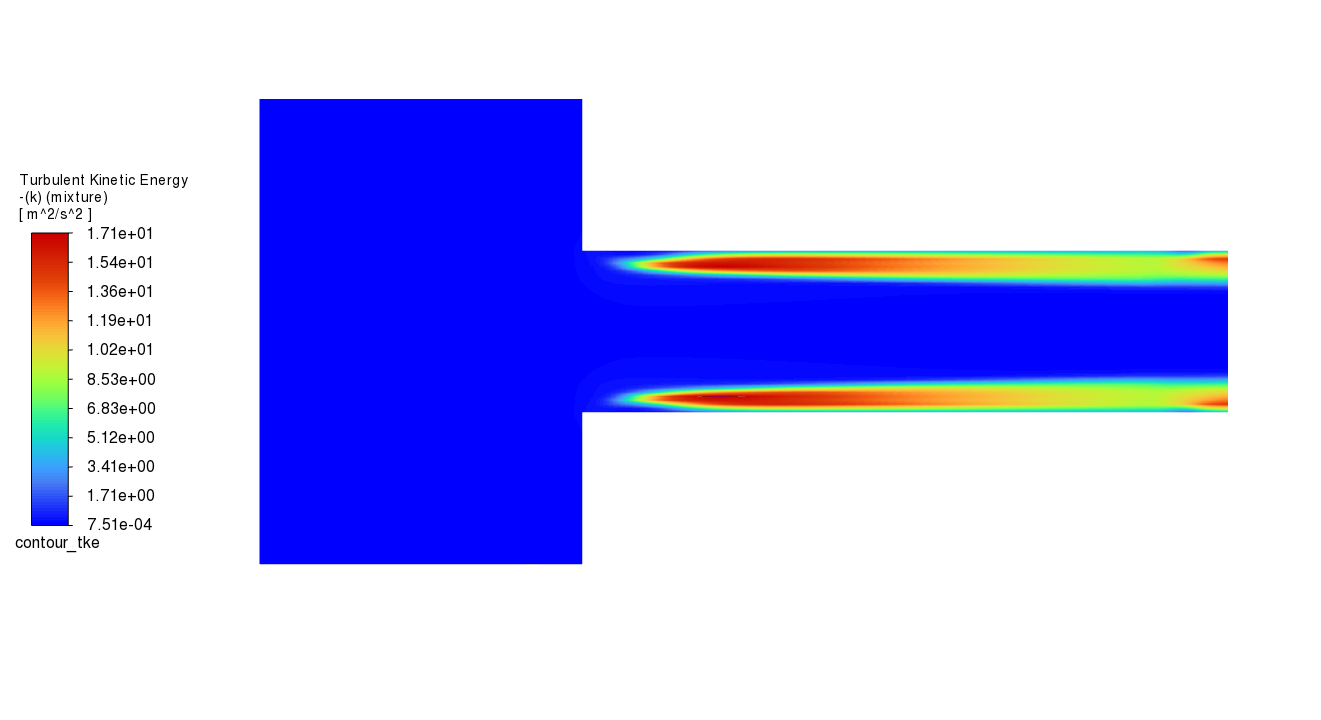
graphics.contour.create("contour_vf_vapor")
graphics.contour["contour_vf_vapor"] = {
"coloring": {
"option": "banded",
"smooth": False,
},
"field": "vapor-vof",
"filled": True,
}
graphics.contour["contour_vf_vapor"].display()
graphics.picture.save_picture(file_name="contour_vf_vapor.png")
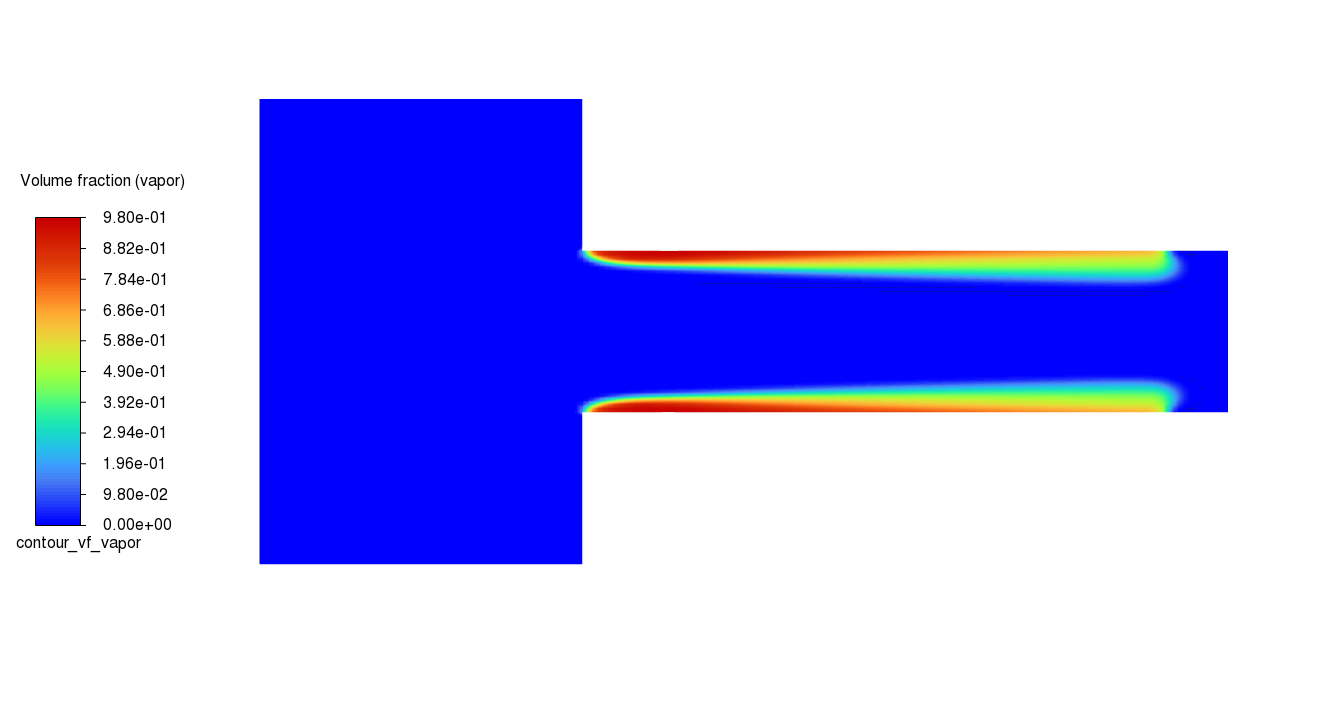
# Save case to 'cav.cas.h5' and exit
solver_session.settings.file.write_case(file_name="cav.cas.h5")
solver_session.exit()

